Pattern matching
Pattern matching in function definition Pattern matching consists of
- specifying patterns to which some data should conform
- and then checking the shape of input data
- and deconstructing the data according to those patterns.
lucky :: Int -> String
lucky 7 = "LUCKY NUMBER SEVEN!"
lucky x = "Sorry, you're out of luck, pal!"
During execution, the patterns will be checked from top to bottom and when it conforms to a pattern, the corresponding function body will be used.
Which is similar to piecewise function in mathematics below:
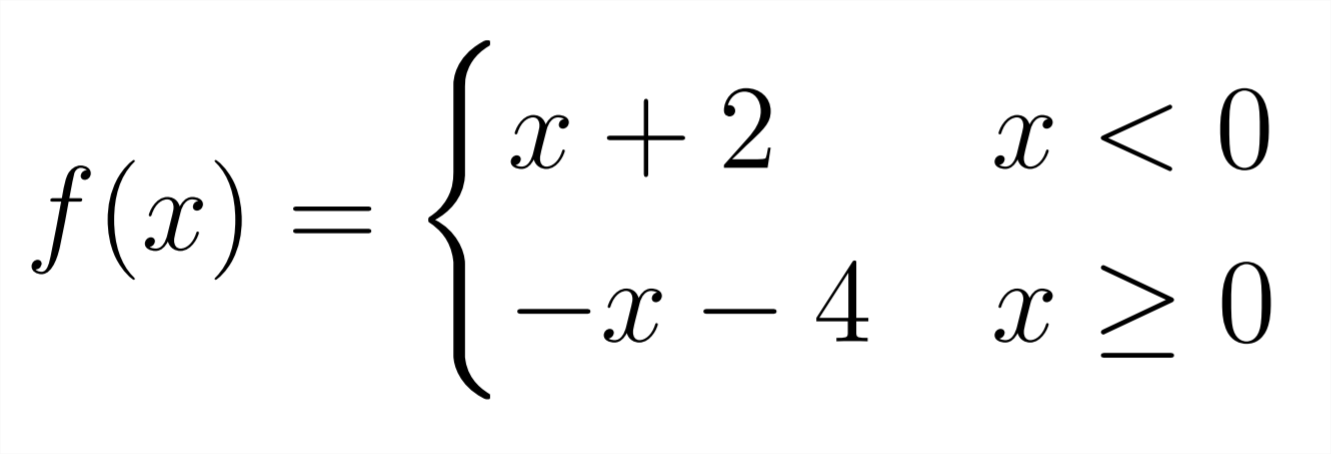
catch-all pattern
binding
deconstructing
ignore with _
pattern matching on Array
takeFive :: Array Int -> Int
takeFive [0, 1, a, b, _] = a * b
takeFive _ = 0
The first pattern only matches arrays with five elements, whose first and second elements are 0 and 1, respectively. In that case, the function returns the product of the third and fourth elements. In every other case, the function returns zero.
- List supports proper pattern matching (Cons/Nil).
- Array does not support pattern matching directly; use uncons instead
pattern matching on Records
pattern matching on List
A pattern like x:xs will bind the head of the list to x and the rest of it to xs, even if there's only one element so xs ends up being an empty list. Note: The x:xs pattern is used a lot, especially with recursive functions.
Pattern matching used outside of function, is not just limited in function
- case
- ADT